IBM’s Digital AI Cores Approach
In recent announcement for its investment in New York state area on AI hardware development, IBM once again touched on the topic of its Digital AI cores researches.
That is why we decided to include some information in our blog on this science approach and its capability to bring change in the future.
Important to know from the beginning is that the so called high performance computing systems has been using high precision 64- and 32-bit floating point arithmetic for its purposes. These large algorithms are critical in the fields, where the accuracy is a must like aeronautics or healthcare. However, there have been large discussions on the topics whether most of the AI focus areas like image recognition and language translation for instance need such rate of precision. Thus the development of the so called approximate techniques that allow most of these tasks to be computed on an acceptable precision level.
Computational building blocks with 16-bit precision engines are typically 4 times smaller than comparable blocks with 32-bit precision. This gain in area efficiency directly translates into a significant boost in performance and power efficiency for both AI training and inference workloads.
As a result one trades numerical precision for computational throughput enhancements by compensating with algorithms to keep model’s accuracy. Here is IBM’s view on the topic:
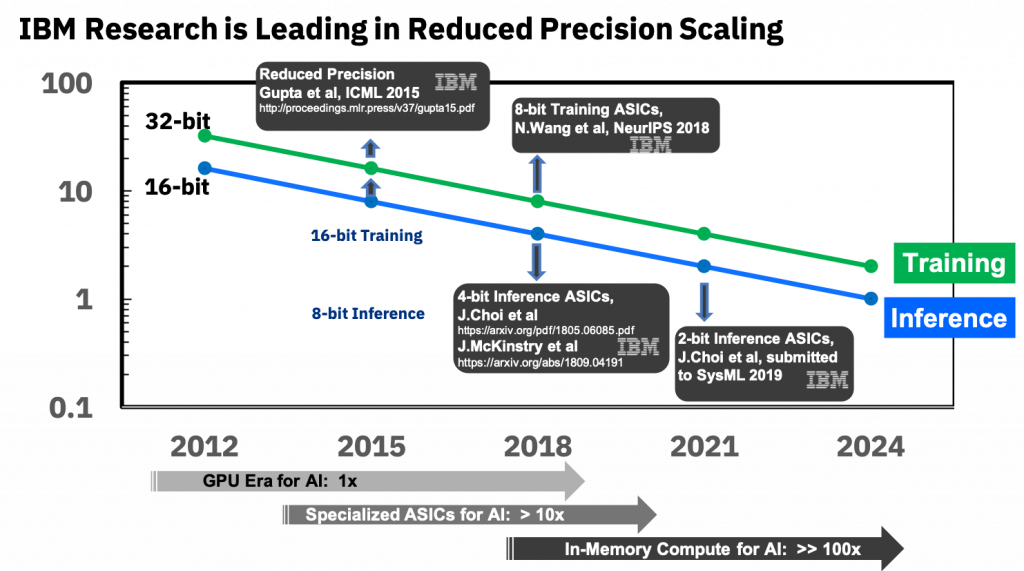
In 2015, IBM announced for the first time and demonstrated that precision of deep learning training systems could be reduced from 32 bits to 16 bits and still fully preserve model accuracy. As expected the approach spread quickly over the industry.
IBM now claims to have broken the next big barriers for low precision, achieving 8-bit precision for training and 4-bit precision for inference, across a range of deep learning datasets and neural networks.
Unlike inference, training with numbers represented with less than 16 bits has been very challenging due to the need to maintain fidelity of the gradient computations and weight updates during back-propagation.
L3C as an IBM PowerCloud provider offers instances on IBM POWERAI package for deep and machine learning.






